 INGREDIENTS
INGREDIENTS
Phosphatidylcholine, deoxycholic acid, caffeine, levocarnitine, methylsilanol mannuronate, and 1 Biomimetic peptide:
Tripeptide-41.
Fill in the form below to access all information about this product.Already a member? Login to access hidden info
COSMECEUTIC AND THERAPEUTIC DIRECTIONS
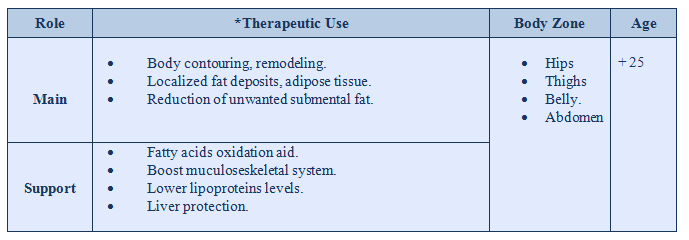
This product is able to create several mechanisms to mainly increase adipolysis and adipocytolysis effect due to its principal components Phosphatidylcholine and Deoxycholic acid. The mechanism implies gene expression of hormones and lipolytic effect and also lysis of the adipocyte membrane. On the other hand the product is reinforce by the biomimetic action of  witch acts by several cellular receptors of cytokines involved in lipid accumulation, lipid synthesis and adipocyte differentiation.
witch acts by several cellular receptors of cytokines involved in lipid accumulation, lipid synthesis and adipocyte differentiation.
It has got other ingredients that help to better recover treatment area and also has got carnitine as a key factor to help liver to eliminate fatty acids and thus protect it to be exposed to high fatty blood levels that may damage liver.
*These are advisable therapeutic uses, but the ingredients of products may allow a physician to apply them under professional criteria, may find the product optimal to treat other aesthetic issues.CLINICAL DATA
Pharmacology
Pharmacology of the actives compounds in the formula which promotes lypolitic effect:
Phosphatidylcholine/Deoxycholic acid: PC/DA
- Injection of phosphatidiycholine (PC) and deoxycholic acid (DA) preparation is widely used as an alternative to liposuction for the reduction of subcutaneous fat. Nevertherless its physiological mechanism of action are not yet fully understood. There are scientific studies about phosphatidylcholine and deoxycholic acid injected into adipose tissue. Phosphatidylcholina decreases adipose tissue mass but deoxycholic acid decreases DNA mass. Both phosphatidylcholine and deoxycholic acid reduce mRNA expression of adipose tissue hormones, such us adiponectin, leptin, and resistin. In lipolysis-related gene expression profiles, Phosphatidylcholina incrased hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) transcription and decreased the expression other lipases, perilipin, and the lipogenic marker peroxisome proliferator activate receptor γ-PPAR. Deoxycholic acid treatment diminished them all, including HSL. Meanwhile the gene expression of pro-inflamatory cytokines are elevated in both phosphatidylcholine and deosxychlic acid injections. Microscopic observation shows that phosphatidylcholine induced lypolisis with mild PMN (neutrophils) infiltration.
- Deoxycholic acid do not induce lipolysis but induces much amount of PMN infiltration.
- In conclusion Phosphatidylcholine alone induce lipolysis in adipose tissue, whereas deosxycholic acid alone might induce tissue damage
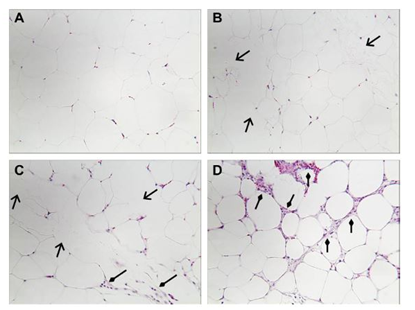
As shows in the stained sections of adipose tissue from saline solution (A) with no infiltration of neutrophils, but (C) phosphatidyl choline indicates adipocyte lipolysis and (C) Deoxycholic acid stained indicates strong neutrophils infiltration.
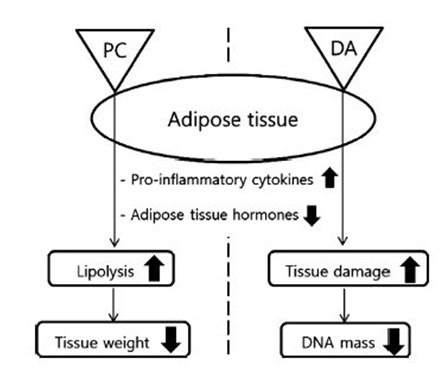
- A working model of phosphatidylcholine or deoxycholic acid on adipose tissue:
Phosphatidylcholine (PC) or deosxycholic acid (DA) on adipose tissue leads to an alteration of expression in pro-inflamatory cytokines, lipases and adipose tissue hormones. However phospahtidycholine and deoxycholic acid differently acts on respective pro-inflammatory cytokines, lipases and adipose tissue hormones, wich led to significant difference in tissue morphology.
Phosphatidylcholine resulted in tissue weight loss via enhancing lipolysis while Deoxycholic acid resulted in tissue damage with reduction of DNA mass.
- Phosphatidylcholina also is very important in the compounding due to its key role in adipolysis injection acting as a vehicle for deoxycholic acid diffusion beyond the injection site due to liposome formation, and mitigating the rate of immediate loss of cell viability. For instance, while injection of deoxycholic acid leads to inmediate cell wall lysis, the onset of PC/DC is delayed after 2-4 weeks after treatment. That’s why is allways better to inject mixture of phospatidylcholine / desoxycholic acid than deoxycholic acid alone to avoid fast cell wall lysis.
- The treatemt should be done with a 2- 4 weeks interval between each session.
Caffeine:
- Caffeine increases lipolysis, raises cyclic adenosine monophosphate cAMP by inhibitin phosphodiesterase PDE, increasing catecholamine release (epinephrine) by simphathetic nervous system. A significant increase in free fatty acid oxidation over physiologic levels is determined.
- Recently, several studies showed that its consumption is associated with lower risk for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), an obesity-related condition that recently has become the major cause of liver disease worldwide. Although caffeine is known to stimulate hepatic fat oxidation, its mechanism of action on lipid metabolism is still not clear. Here, we show that caffeine surprisingly is a potent stimulator of hepatic autophagic flux. Using genetic, pharmacological, and metabolomic approaches, we demonstrate that caffeine reduces intrahepatic lipid content and stimulates β-oxidation in hepatic cells and liver by an autophagy-lysosomal pathway. Furthermore, caffeine-induced autophagy involved down-regulation of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling and alteration in hepatic amino acids and sphingolipid levels. In mice fed a high-fat diet, caffeine markedly reduces hepatosteatosis and concomitantly increases autophagy and lipid uptake in lysosomes.
Methylsilanol Manuronate:
- Silicon is a constitutive element of the cutaneus connective tissue which takes part in the formation and organization of extracellular matrix (ECM). The natural concentration of Si decreases with aging and leads to tissue destructuration: age skin and wrinkles.
- Silanols are capable to substitute that loss of silicon an thus help in restructuring connective tissue by slowing down the effects of aging.
- The activity of silicon has been proven through the restructuration of connective tissue and the multiple effects: antiwrinkles, firming, stimulation, moisturization, ..)
- Silanol activities on collagen production i.e. firming and young skin aspect, is a direct consequence of their cytostimulating effects demonstrates on fibroblasts cultures.
L-carnitine:
- Using this substance for weight loss encourages the metabolism of fat by helping the transfer of fatty acids to the power houses of the cells, the mitochondria. It increases the body’s ability to release stored fat in the form of triglycerides which provide more energy to the body.
- It is essential this ingredient due to the strong adipolysis effect caused by mainly phosphatidylcholine, releasing fatty acids to the blood circulation and then they reach the liver and then converted into energy in the mitochondria. If we not help to eliminate that higher blood concentration of fatty acids in the liver, the organ may be damage during the treatment.
- Carnitine improves protein accretion, muscle mass, and protein fat accretion in piglets.
- Carnitine may have beneficial effects on skeletal muscle mass through stimulating the anabolic IGF-1 pathway and suppressing pro-apoptotic and atrophy-related genes, which are involved in apoptosis of muscle fibers and proteolysis of muscle proteins, respectively.

- This singular peptide of 3 aminoacids, helps to restrain accumulated lipid and promotes lipolysis.
- It is well proven that this peptide decreases lipid droplet formation wich implies antidifferentiation effect on pre-adipocyte. The lipid synthesis inhibition is showed in a dose dependent pathway.
- This peptide has a important role at inhibition of adipocyte differentiation due to its activity on ARK 1 and ARK2 kinases. These kinases play a specific and important role at cell cycle progression. As a consequence of that blocking of kinase action the transcription factor C/EBP alfa is also blocked. This factor is involved in lipid metabolism for converting free fatty acids into Triglycerides in the mitochondrion thus avoid lipid accumulation.
- This tripeptide acts by stimulating the macrophage kinase receptor that activate Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) biosynthesis and as a consequence increasing adipocyte lipolysis.
Posology and way of administration
They should be done by the supervision of a doctor or a registered nurse and they will apply the best technique available in each case.
The product is developed sterile, preservative free and pyrogen free to be used on several aesthetic techniques, IPL, roller and other invasive or no invasive procedures.
References:
(1) TNF-alpha induction of lipolysis is mediated through activation of the extracellular signal related kinase pathway in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
J Cell Biochem. 2003 Aug 15;89(6):1077-86.
(2) EBPalpha motifs regulate lipogenic and gluconeogenic gene expression in vivo
EMBO J. 2007 Feb 21;26(4):1081-93. Epub 2007 Feb 8. Distinct C/
(3) Caffeine stimulates hepatic lipid metabolism by the autophagy-lysosomal pathway in mice.
Hepatology. 2014 Apr;59(4):1366-80. doi: 10.1002/hep.26667. Epub 2014 Feb 18.
 English
English